The Convergence of AI and Cybersecurity
 AI and Cybersecurity
AI and Cybersecurity
Are Artificial Intelligence (AI) and related technologies going to ultimately help us or harm us? It’s a question being debated across news cycles and behind closed doors on Capital Hill as AI technologies continue to be developed and implemented at an unprecedented rate, with little legislation, controls, or governance. And the market is booming. Goldman Sachs forecasts AI investments to reach around $200 billion globally by 2025, and Forbes is expecting an annual market growth rate of 37.3% over the next seven years.
You may already be familiar with some of the more popular forms of AI technology that have been written about about in the news: ChatGPT, a chatbot known for it’s ability to code software, successfully pass the Bar exam, and have convincing human-like chat conversations. There are also malign uses for this technology such as allowing someone with relatively little effort to make DeepFakes, convincing but entirely counterfeit images or even video of a person ‘spliced’ into a preexisting image or video.
There are also AI technologies in use that may not be as apparent like the voice-assistant on your smartphone, or an online customer service ‘assistant’ who can process refunds for an online purchase. As of today in late 2023, https://theresanaiforthat.com (an online database for AI technology) lists 8,700 AI products that are trained for 2,300 specific tasks and directly impact or fulfill tasks across 4,800 jobs performed by humans.
In the realm of cybersecurity, AI provides benefits to both security teams and cybercriminals. In a classic game of “cat and mouse”, hackers use AI to build better password-guessing tools and generate authenticate-looking ploys that mimic, for example, a sender’s email message with customized wording, fewer grammatical issues and tell-tale indications of a phishing expedition. The latest news headlines already indicate AI is actively used by hackers: prompt hacking and malicious software creation. What’s ahead: cybercriminals will use AI-based tools to develop new and more intelligent malware then test the success of their product against AI tools.
At the same time “Cyber AI” will enable security teams to anticipate cybersecurity threats and incidents, then respond faster to compromises. For example, a AI security bot could recognize a phishing attempt and stop a message before it hits a person’s inbox. Organizations could use AI to prepare for AI-driven cybercrimes with accelerated threat detection. Instead of being in a constant reactive environment, the new security efforts can be proactive.
AI offers human agents the ability to collaborate, detect and prevent compromises, limiting an organization’s exposure. Machine learning and natural language processing, elements of AI, will help security teams to detect actual threats from “noise.” A collaborative effort of human and machine interaction can enable better pattern recognition, threat prediction, and adaptability then generate faster and more accurate responses.
But it’s important to remember this market is still quite early in it’s lifecycle. These examples above are only the very beginnings of AI integration in use. Large investments in AI technology are occurring across every major sector from healthcare and transportation to finance and education, which will bring their own sets of unique potential benefits or opportunities for misuse.
As policy makers today scramble to build a framework for broadly governing AI integration, on a day-to-day scale it is much less clear what AI will be capable of going forward, how they will be implemented, and what outcomes it will lead to. While It’s important to stay informed about the ongoing evolution of AI and cybersecurity, there are some steps you can take towards protecting yourself and benefiting from AI technologies:
- Be selective about using products with AI capabilities. Look for providers who are transparent about how they develop and audit their AI systems. Avoid any tools or services that make overbroad claims about AI.
- Consider any potential privacy risks ahead of time. Read the “Privacy Policy” documentation and understand how your information is used by any AI systems you interact with before using an AI product or service.
- Practice good cyber hygiene. Use strong, unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for your online accounts and services when possible.
- Watch out for phishing attempts and verify the identity of any party requesting personal data or information.
- Advocate for responsible and thoughtful governance of AI development and use with state and local representatives. As consumers and citizens, we have the ability to influence the policies and regulations being developed to address the potential benefits and risks of AI use.
Refererences and Further Reading
Protecting Your Digital Life: Cybersecurity Tips While Traveling

In today’s hyper-connected world, travel often means staying connected to the digital realm. Whether you’re traveling for business or leisure, it’s crucial to prioritize cybersecurity to protect your personal and sensitive information from cyber threats. Here are some cybersecurity tips to keep in mind while you’re on the go:
- Travel As Light As Possible: Take only the devices you will need. The more devices you take with you, the more you risk losing them or having them stolen.
- Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN): Before you embark on your journey, invest in a reliable VPN service. A VPN encrypts your internet connection, making it much harder for hackers to intercept your data. It also allows you to access geo-restricted content safely.
- Update and Secure Your Devices: Ensure that all your devices, including smartphones, laptops, and tablets, are up-to-date with the latest security patches and software updates. Enable strong, unique passwords and use biometric authentication when possible.
- Check privacy & security settings: Make sure your web services and apps are not sharing your locations or other sensitive information. You may want to turn off some features, like location tracking, while you are traveling.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Whenever possible, enable 2FA for your online accounts. This adds an extra layer of security, making it much harder for unauthorized users to access your accounts.
- Backup Your Data: Before your trip, back up your data to an encrypted external drive or a secure cloud service. This ensures that you won’t lose critical information in case of theft or device damage.
- Be Careful What You Post: Do not advertise that you are not going to be home before you leave. While traveling, don’t advertise the fact that you are not at home.
- Disable Automatic Connections: Turn off Wi-Fi and Bluetooth when not in use. Hackers often target open Wi-Fi networks in airports, cafes, and hotels. If you need to use public Wi-Fi, connect through your VPN for added security.
- Beware of Public Charging Stations: USB charging stations in airports and other public places can be compromised to steal your data or install malware on your device. Use your charger and a wall outlet whenever possible.
Multifactor Authentication and why it is important
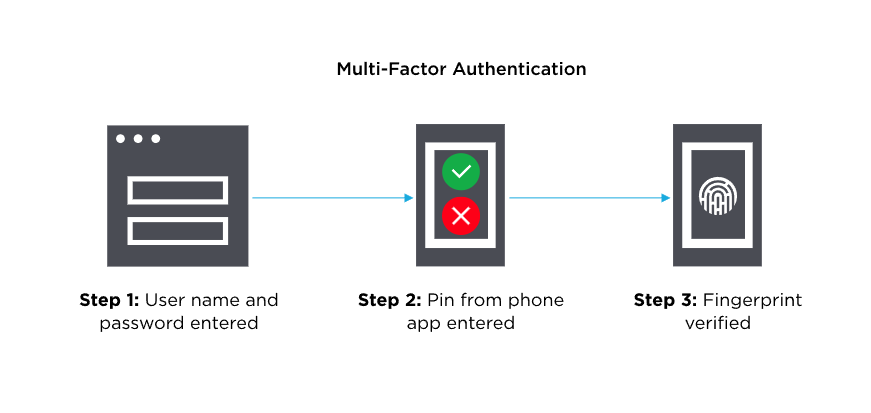
Many people are seeing more and more services requiring or suggesting the use of multifactor authentication (MFA) for accessing online systems. MFA is a login process that requires multiple methods of authentication to verify a user’s identity. It combines two or more independent credentials to verify a login.
- The first credential is based on something the user knows. Typically, it requires the user to answer a personal security question. This can be in the form of a password, personal identification number (PIN), or a one-time password.
- The second credential is based on something that only the user can access, such as their personal phone or tablet. Things like a badge, token, key fob, or even just your phone all would meet the requirement to be a credential here. One common method will send your phone a text with a code for you to enter before continuing while logging into the service.
- The third credential is something that is physically distinct for each user, also known as the inherence factor. Fingerprints, iris scans, or facial recognition are all examples, however, a third type is rare unless the data being accessed is highly sensitive. Although sometimes this type of verification will be used in place of the second type, very much like your phone’s ability to access secure content with your Face ID.
No matter the type of verification, multifactor authentication adds an extra, usually quick, step when logging into secure sites. This extra step adds a good deal of security to your accounts and great peace of mind.
Multifactor authentication is being used to help increase the security of your accounts and services that may potentially contain sensitive information. MFA helps validate that the person who is accessing the account is an authorized user. It adds another layer of defense for your account, making it harder for someone to gain unauthorized access. This additional layer of defense helps protect you against weak or stolen passwords. NordPass, a security and privacy-focused company, found that “123456”, “password” and “qwerty” are some of the most commonly used passwords in 2022. These types of common passwords are very easy to guess or crack, and just having MFA turned on for those accounts helps keep malicious people out of accounts.
In conclusion, while MFA may take a few extra seconds to verify your identity, the added layer of security makes it that much harder for cyber-criminals to access your private and sensitive data. By verifying your credentials using a method that is physically tied to your person, such as your phone or your Face ID, companies can ensure that your data is that much safer from prying eyes. Please feel free to contact your Computer Support Specialist if you have any questions.
How to protect your phone or tablet – simple steps for Android and iOS security.
Phones and tablets have gone from being cool gadgets to our partners in crime, helping us keep in touch with our people, hoarding our secrets, and occasionally granting us entry into the mystical realm of work networks and services. They’re like little digital treasure chests of personal data.
But, just like we’d lock up our physical treasures, it is essential to secure our digital loot. We don’t want any tech-savvy pirates plundering our data and causing virtual mayhem. Whether you use an Android or Apple, your phone or tablet deserves a sturdy digital lock to keep it safe.
In this article, we will go over things you can do to bolster the security for your trusty devices.
1. Keep Your Operating System Up to Date
Both iOS and Android regularly release updates to improve security, squash various software bugs, and fix vulnerabilities. It’s important to keep your device’s operating system (OS) up to date. Here’s how:
- For iOS: Go to “Settings” > “General” > “Software Update” and follow the on-screen instructions to install the latest updates.
- For Android: Navigate to “Settings” > “Software Update” and check for available updates.
2. Use Strong Passcodes or Biometrics
Setup a strong lock screen to your device. Choose a PIN, password, or use a biometric method like fingerprint or facial recognition.
- For iOS: Go to “Settings” > “Face ID & Passcode” or “Touch ID & Passcode” and follow the instructions to set up a secure passcode or biometrics.
- For Android: Navigate to “Settings” > “Security and Privacy” > “Screen lock” to choose between PIN, password, or biometric options.
3. Regularly Review App Permissions
Apps on your device may request access to various features and data. Review and limit app permissions to protect your privacy. Do apps like Facebook and Amazon always need access to your location, for instance?
- For iOS: Go to “Settings” > “Privacy & Security” to view which apps have access to your location data, camera, your contacts, and the like.
- For Android: Navigate to “Settings” > “Apps” > [App Name] > “Permissions” to manage app permissions.
4. Regularly Back Up Your Data
Backing up your device regularly will ensure that you don’t lose your data if the phone is broken, lost, or otherwise compromised.
- For iOS: Go to “Settings” > [Your Name] > “iCloud” > “Backup” and enable iCloud Backup.
- For Android: Navigate to “Settings” > “Accounts and Backup” and turn on “Back up to Google Drive.”
Going over these steps will strengthen the security of your iOS or Android phone and tablet. Remember that cybersecurity is an ongoing process, so stay vigilant in protecting your personal information and digital assets. Taking these precautions will help you enjoy the benefits of your devices while keeping your data safe and secure. Please let us know if you have any questions or need help with any of these steps.
Updating Computer Software
According to the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, users should do three things regarding computer updates. First, turn on automatic updates. This downloads important software updates in the background while you work. Second, watch for notifications. The update will let the user know when the updates are ready to install. Third, users should install updates as soon as possible. This ensures that security holes are patched as quickly as possible.
Updating your computer software has three benefits. First the updates will fix bugs in the software that causes glitches and security problems. Second, software updates improves performance of the operating system and all software on the computer including drivers and firmware. Lastly, updates will install the latest features available for your system.
Laptops and Desktops
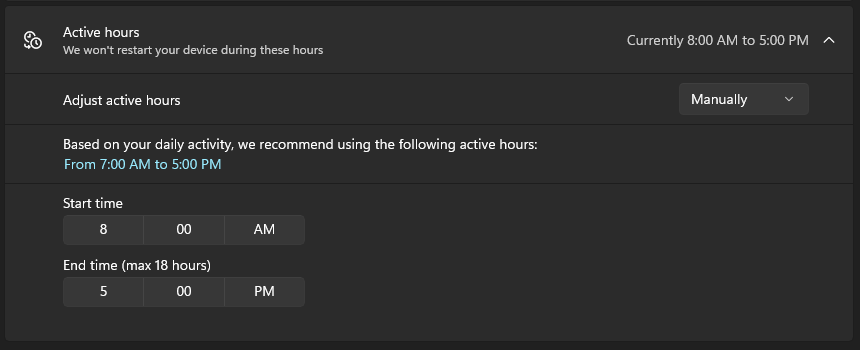
After running the updates, be sure and restart your computer to install the patches and give your computer a fresh reboot. You can also schedule an update and restart. In Windows Update, schedule your Active Hours so your computer only restarts after you leave the office. To do this navigate to Windows Update, Advanced Options, Active Hours.
Mobile Devices
For mobile devices and apps the above guidelines also apply. Using your device’s “update” feature in both the general settings and app store ensures your phone or tablet is up to date and secure with the latest features.
In addition to software updates, Apple has implemented Rapid Security Response technology to bring security patches in between full updates for iPhones and iPads. This ensures your mobile device will have security updates as quickly as they are available. To turn on Rapid Security Response do the following:
- Go to Settings > General > Software Update.
- Tap Automatic Updates.
- Make sure that Security Responses & System Files is turned on.
Summary
Updating your software regularly will keep your computer and mobile device secure and performing the best that it can.
Sources
https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/news/understanding-patches-and-software-updates
https://www.nist.gov/blogs/cybersecurity-insights/cybersecurity-awareness-month-2022-updating-software
https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT204204